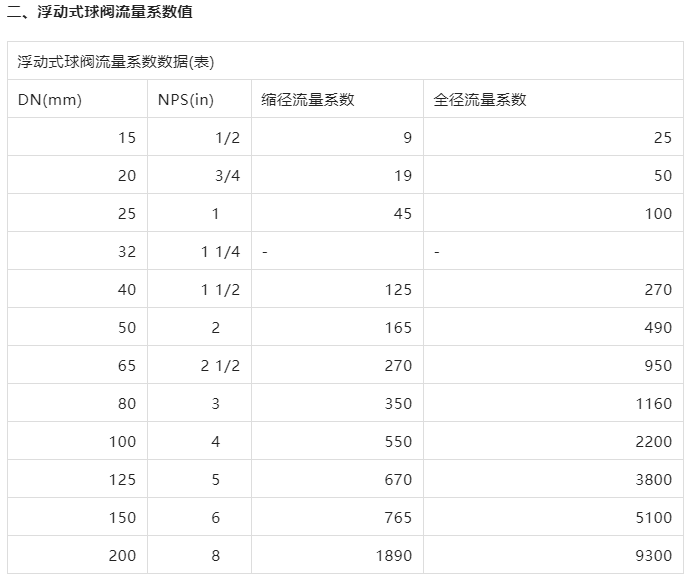
Floating ball valve flow coefficient table
First, the floating ball valve flow coefficient description:
There are many factors influencing the flow coefficient of floating ball valves, such as the size, structural form, valve type, specification, pressure and other factors of floating ball valves.
The flow coefficient of a floating ball valve refers to the volumetric flow, or mass flow, of the pipe medium flowing through the floating ball valve over a unit period of time, under test conditions. That is, the maximum flow capacity of the floating ball valve.
A higher flow coefficient value indicates less pressure loss as fluid flows through a floating ball valve.
The flow coefficient is: C value (European and American standards are called Cv value, international standards are called: KV value) is an important process parameter and technical index of industrial floating ball valves such as floating ball valves and regulating valves.
Correct calculation and selection of CV value is an important step to ensure the normal operation of pipeline flow control system.
The inherent Cv value of the floating ball valve itself cannot be calculated, and it is obtained experimentally. The above data calculates the Cv value required for this medium to flow through the floating ball valve, and the Cv value floating ball valve to meet it, then whether the Cv value of the floating ball valve meets it, then the floating ball valve should be taken to the experiment, or the floating ball valve is 3D drawn with computer simulation to estimate the inherent Cv value of the floating ball valve.
The inherent Cv value of the floating ball valve represents the flow capacity of the floating ball valve, which is only related to the internal structure of the floating ball valve, that is, the shape and size of the place where the medium flows, and has nothing to do with anything else. As for the small deformation of floating ball valves caused by thermal expansion and contraction, they are not considered, because the standard stipulates that the medium for testing the flow capacity of floating ball valves is pure water at 60 degrees.
The flow coefficient indicates the flow rate of fluid when the fluid flows through the floating ball valve to produce a unit pressure loss, and the flow coefficient has several different codes and magnitudes due to the different units.
General Formula:
C=Q√p/P
C--- Flow coefficient
Q--- Volume flow
p--- Fluid density
P--- Floating ball valve pressure loss
The table below shows the flow coefficient for floating ball valves, where the Cv value represents the number of gallons per minute of water flowing through the valve at +60°F (+16°C) at a pressure drop of 1 pound/in2 (0.006894757MPa).